The research focuses on tunable plasmonic HfN nanoparticles and arrays and demonstrates the possibilities for development and fabrication of such nanostructures.
In the recent years unconventional plasmonic materials such as the group-4 metal nitrides (including HfN) have been attracting strong interest for their compelling qualities. Similarly to silver and gold, they feature visible light absorption cross sections, but also demonstrate additional benefits of high melting point, chemical stability and mechanical hardness. As such metal nitride nanoparticles are likely to demonstrate more stable and reliable optical properties.
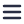
Even though this material is very promising, there are only a few reports on the fabrication of such nanoparticles. The authors explore and develop lithographic preparations for creating such structures, and also analyse the achieved properties of localised surface plasmon resonances (LSPRs) with cathodoluminescence (CL) spectroscopy. Cathodoluminescence imaging was performed with the SPARC system, and the acquired CL maps in the visible range demonstrated clear surface plasmon resonances.
The experiment demonstrates that HfN nanoparticles can be a feasible and possibly a better alternative to classical noble metal nanostructures, particularly in plasmonically-powered applications where materials robustness is important. To read the full paper please go here.
.png)