This results in a high-resolution 3D structure of a protein complex in its near-native conformation. Depending on the quality of the reconstruction, subtomogram averaging can yield structures with near-atomic resolution. The quality of the reconstruction is dependent on nearly all steps in the cryo-ET workflow. Here we will highlight some of the most important parameters that influence the quality of the reconstructions.
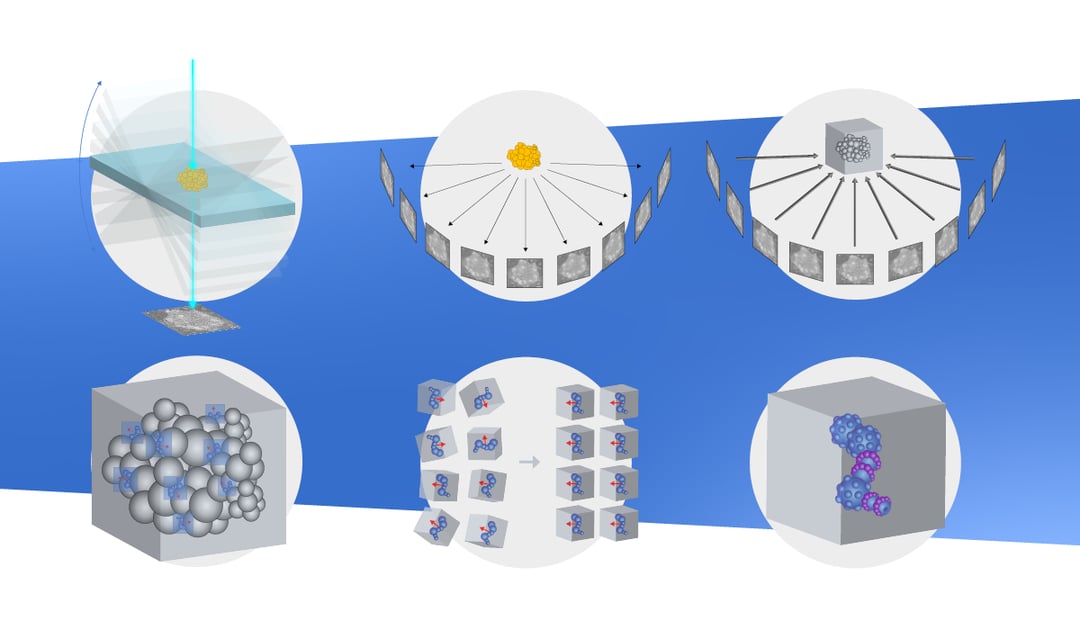
 Tomograms are usually acquired from sections about 100-300 nm thick. The section is imaged at different tilting angles, typically in the range of -60° to 60°. The resulting set of images is called a tilt series. Imaging the same area multiple times results in radiation damage to the sample due to electron exposure. For this reason, tomograms are often acquired at lower electron doses than conventional TEM. However, even with a lower electron dose, the sample is gradually damaged during imaging, leading to a loss of information at the end of the tilt series acquisition. Another consideration is that the highest resolution information is acquired when imaging at low angles, since at higher angles the relative thickness of the section increases.
Tomograms are usually acquired from sections about 100-300 nm thick. The section is imaged at different tilting angles, typically in the range of -60° to 60°. The resulting set of images is called a tilt series. Imaging the same area multiple times results in radiation damage to the sample due to electron exposure. For this reason, tomograms are often acquired at lower electron doses than conventional TEM. However, even with a lower electron dose, the sample is gradually damaged during imaging, leading to a loss of information at the end of the tilt series acquisition. Another consideration is that the highest resolution information is acquired when imaging at low angles, since at higher angles the relative thickness of the section increases.
Taking together the increase in damage over time as well as the fact that most information is obtained at low angles, most researchers use a so-called “dose-symmetric” approach during acquisition. In this strategy, the low angles in both positive and negative tilt are imaged first in an alternating fashion, ensuring the data loss is constrained to the higher angles, leading to higher quality data [1].
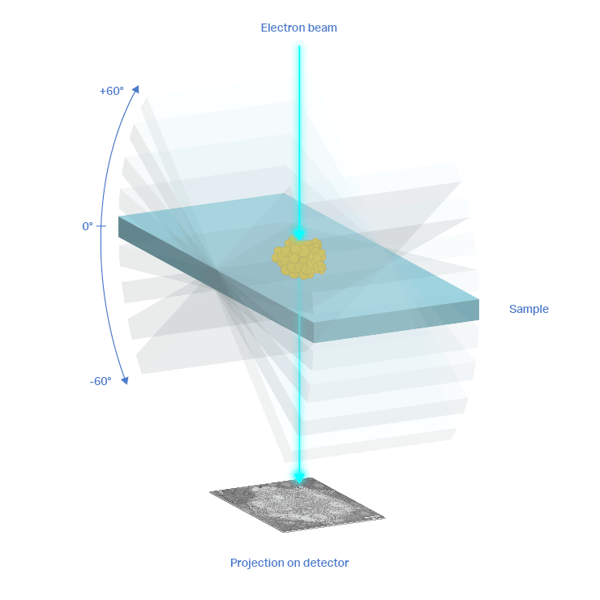
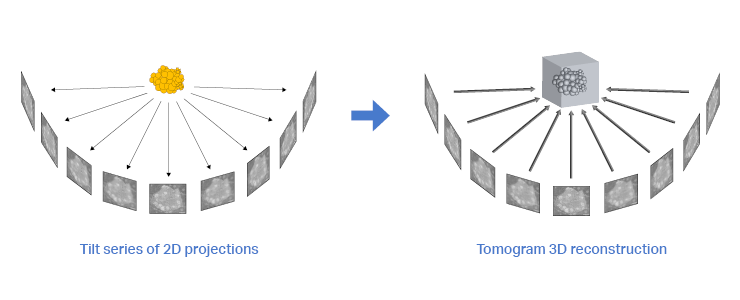 After the acquisition, the tomogram needs to be processed to allow subtomogram averaging. As a first step, some corrections have to be made to compensate for stage drift and beam drift that occurs during acquisition. Next, each projection needs to be properly correlated to the rest. Each image in the tilt series is a projection of the volume from a different angle. The relative angles, translations, and rotations between all projections need to be determined exactly. This is done in a process called tilt series alignment.
After the acquisition, the tomogram needs to be processed to allow subtomogram averaging. As a first step, some corrections have to be made to compensate for stage drift and beam drift that occurs during acquisition. Next, each projection needs to be properly correlated to the rest. Each image in the tilt series is a projection of the volume from a different angle. The relative angles, translations, and rotations between all projections need to be determined exactly. This is done in a process called tilt series alignment.
Tilt series alignment can be made easier by including fiducial markers in the sample [2][3]. Most used fiducials are 5-10nm gold beads that assist in correlating the individual images of the tilt series. Alignment without the use of fiducials, or “markerless alignment”, is also possible and relies on features within the images [4] or on the correlation between images [5].
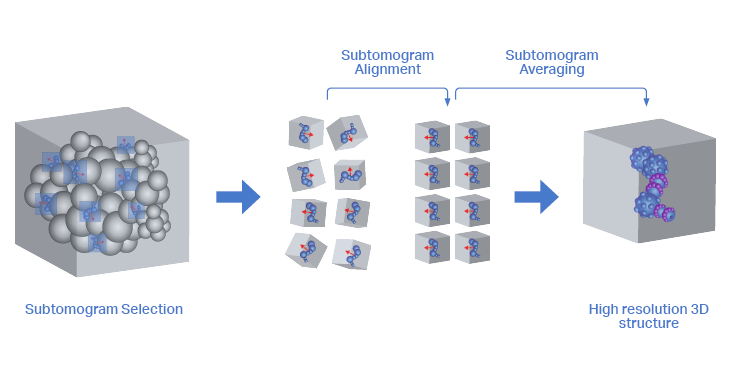 Next, the tilt series needs to be converted into a 3D reconstruction. The development of better and faster reconstruction algorithms is an ongoing process that seeks to extract the most data from the tilt series while trying to conserve resolution and contrast. In this section, we will not go deeper into reconstruction algorithms, but several interesting reviews are available [6]–[9]. The resulting 3D reconstruction can then be used for subtomogram averaging.
Next, the tilt series needs to be converted into a 3D reconstruction. The development of better and faster reconstruction algorithms is an ongoing process that seeks to extract the most data from the tilt series while trying to conserve resolution and contrast. In this section, we will not go deeper into reconstruction algorithms, but several interesting reviews are available [6]–[9]. The resulting 3D reconstruction can then be used for subtomogram averaging.
For a high-resolution 3D structure of the protein complex of interest, at least 1000-2000 copies of the protein complex need to be averaged. Finding and selecting these is known as particle picking. Particle picking can be done manually, which is a very laborious process. Fortunately, several types of automated particle picking are also available.
Automated particle picking can be assisted by features such as membranes or microtubules along which the protein complexes can be found [10][11]. Alternatively, automated particle picking can be performed by matching the particle against a known template, often a 3D structure of the protein complex that was resolved in vitro [12]. Lastly, particle picking can be assisted by neural networks that are manually trained using smaller training datasets [13].
When the set of subtomograms is gathered, it needs to be aligned in a way that the 3D structures can be overlayed for averaging. This means that for each subtomogram, the relative angle and translation are determined against a template. The template can be a previously determined 3D structure or an ever-updating model of the averaged subtomograms from the current set [6][9]. In the latter case, averaging subsets of subtomograms in an iterative way determines not only their relative orientation but also updates the template for the next iteration.
When the averaging of the distinct subsets reaches the same template, the iteration stops. During this process, many subtomograms are rejected from the dataset. This can be caused by it not being the correct protein complex, but also when the protein complex is partly obscured by membranes, microtubules, or protein-protein interactions. Lastly, the averaging process iterates through refining steps in which the parameters of the algorithm are adjusted until the highest resolution of the final 3D model is found.
Achieving a high-resolution 3D model of a protein complex in its native state using in-situ cryo-ET is a complicated procedure. The quality of the tomogram and the number of particles play a large role in obtaining a high-resolution structure. So having a higher quantity of good-quality lamellae is desirable. The integrated light microscopy solutions we offer at Delmic greatly increase the chance of localizing proteins of interest for lamellae milling and reduce contamination by decreasing the number of handling steps. This will lead to easier and better tomogram acquisition, and ultimately to higher resolution structure resolving using subtomogram averaging.
References
This work is supported by the European SME2 grant № 879673 - Cryo-SECOM Workflow
.png)